\(\text{Variance}\)¶
You can use the \(\text{Variance}\) function to calculate the variance of a collection of basic values. Values can be provided as parameters or contained within a collection of iterable types.
You can use the \variance backslash command to insert this function.
The following variants of this function are available:
\(\text{real } \text{Variance} \left ( \ldots \right )\)
This function calculates the variance using the relationship:
\[\text{Variance} \left ( X \right ) =
\frac{1}{N} \sum_{x \in X} \left ( x - \mu \right ) ^ 2\]
Note that, like the \(\text{Count}\) and \(\text{Average}\) function, you can use this function to traverse complex data structures to calculate the variance.
Figure 217 shows the basic use of the \(\text{Variance}\) function.
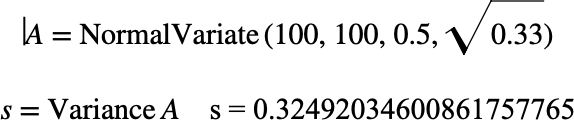
Figure 217 Example Use Of The Variance Function¶
